2. Mammals
There are about 5,700 species of mammals.
They appeared 200 million years ago.
They evolved from a group of reptiles that developed hair
and capacity for feeding their calves with milk that themselves produced.
a) Habitat
They are terrestrial tetrapods.
Some are aquatic (e.g. dolphins) and only one group can fly (bats)
b) Morphological characteristics
- They have four limbs. These extremities are adapted to different ways
to move and can be wings, legs or fins.
- Their body is divided into: head, trunk and tail.
The head is joined to the trunk by the neck.
- Their skin is covered by hairs. They protect of heat loss.
- They have several types of glands: sweat glands, sebaceous glands
and mammary glands.
c) Vital functions:
Nutrition:
The digestive system is complete. They have mouth
with teeth and lips (to suction).
Teeth have different shape depending on the kind of feeding
the animal has.
Anus opens outside directly.
Mammals breathe through lungs.

They have double circulation.
This means that blood follows a double circuit:
- Pulmonary circulation (Heart-Lungs)
- Systemic circulation (Heart- Body)
Their heart has four chambers: two upper atriums and two lower separated ventricles, so that they have complete circulation. This means that oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood don´t mix.
They have two kidneys.
Interaction
They have a well developed brain and sense organs:
eyes (with eyelids), ears (with auricles), taste, smell and touch.
They are homeotherms (warm-blooded). This means that they can keep their body temperature constant.
Reproduction:
Fertilisation is internal.
They are viviparous. Young grow in the mother’s womb (uterus).
Mammals care young and females feed them with milk produced in their mammary glands.
d) Classification:
- Monotremes
They are oviparous.
They have a beak without teeth.

- Marsupials
They are viviparous but calves birth very immature and
have to complete their development inside the mother’s pouch
(marsupium).

- Placentals
Young develop completely inside the mother’s uterus.
Embryo is connected to the female by the placenta.


READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
2.1. Answer the questions about mammal jaws:
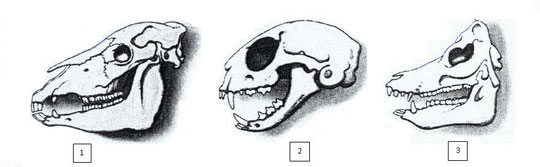
a. Indicate, in each picture, the different types of teeth:
- Incisors (colour them in yellow)
- Canines (colour them in red)
- Molars (colour them in blue).
b. What type of tooth is more developed in every case?
c. We can deduce by the type of dentition, what kind of food they take. Try to identify what of the skulls belong to a carnivorous, to an herbivorous and to an omnivorous.
2.2. Listen and indicate if the described characteristic belongs to:
a. Placentals
b. Marsupials
c. Monotremes

Now,
check
your
answers!

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.

SPEAKING ACTIVITIES
Now, in turns with your partner,
answer the questions in the worksheet.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)





