3.5. Groundwater
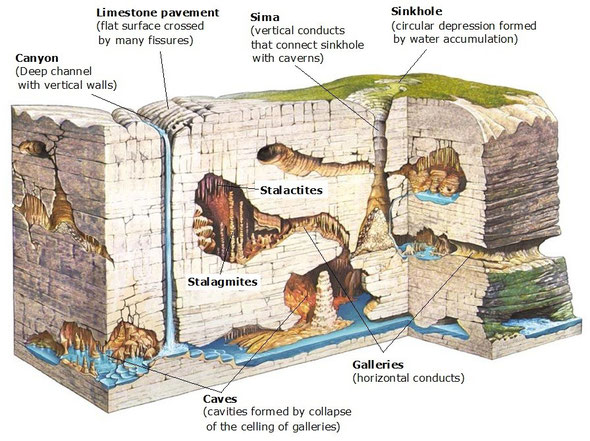
The result of the geological action of the groundwater on or under the surface of the Earth is known as karst landscapes.
It is due to the carbonation, a type of chemical weathering. The rainwater dissolves the carbon dioxide of the atmosphere transforming it in a weak acid that dissolves the calcium carbonate (calcite) found in limestone.
As the acid water penetrates and dissolve the rock very characteristic erosional landforms are formed:
- on the surface we can find sinkholes (or dolines), simas, canyons,
and limestone pavement.
- under the surface water infiltrates throughout the rock and forms caves
(or caverns) and galleries.
The dissolved CaCO3 are deposited in the celling (stalactites) or on the floor (stalagmites) of these underground cavities.
Animation: Cave formation (Classzone)

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.5. What is the difference between stalactites and stalagmites?
Where do you find them?
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




