4. Tissues: asociation of cells.
A tissue is a joint of identical cells that perform the same function and have the same embryological origin.
There are many different kinds of tissues in the human body, but it is possible to group them in four types for their study: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue.
a) Epithelial tissue
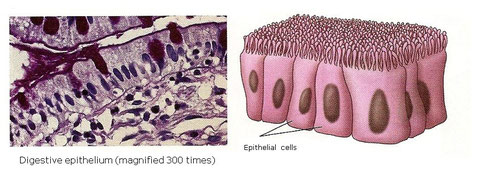
It is formed by polyhedrical cells which are very closely jointed without spaces among them. Usually they are disposed making layers, one on top of the other.
There are two types of epithelial tissues:
Covering epithelium It covers and protects the outside surfaces and inner cavities of our body. Among them there are:
Mucouses. They cover the inner surface of mouth, esophagus, rectum, nasal passages, trachea, etc.
Endothelia. They cover the inner side of blood vessels, heart, etc.
Epidermis. It is the most external layer of skin.
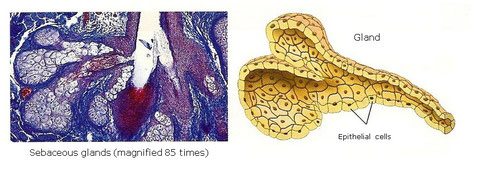
Glandular epithelium. This tissue forms the glands. Glands’ function is secretion of substances. We can distinguish among them:
Exocrine glands. They secrete diverse substances to outside or to internal cavities. Ex: sebaceous glands, salivary glands, etc
Endocrine glands. They secrete hormones to blood. Ex: hypophysis, thyroid, etc.
Mix glands. They have at the same time, exocrine secretion and endocrine secretion. Ex: pancreas.
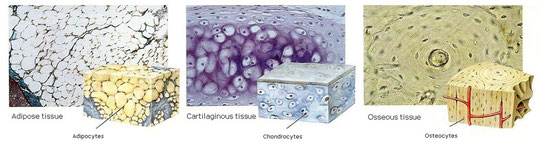
b) Connective tissue
It is formed by little specialized cells immersed in an intercellular substance (extracellular matrix) which contains fibres (collagen, elastin, etc.).
There are several types:
Conjunctive tissue. It is the proper connective tissue. It is located jointing together other tissues and organs. It forms, for example, ligaments and tendons.
Adipose tissue. Their cells, adipocytes, are full of fats. Their functions are lipids storage and thermal and mechanical insulation and protection.
Cartilaginous tissue. The cells which form it, chondrocytes, make cartilage, an extracellular semi-solid and flexible substance. It is the flexible skeleton of nose, trachea, ears and surfaces of joints.
Osseous tissue. It is formed by osteocytes which make a solid extracellular substance compound by mineral salts of calcium carbonate and phosphorous. It forms the bones.
Blood. It is the only liquid tissue. It has three cellular types (red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets), a liquid extracellular substance (plasma) and several kinds of fibres. Its function is to transport substances through the body.
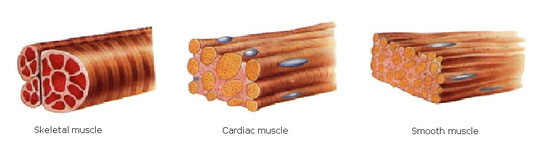
c) Muscle tissue
It is formed by long cells, called muscle fibres. They contain myofibrils (actin and myosin).These protein fibres are responsible for muscle contraction and relaxation. There are three kinds of muscle tissue:
Smooth muscle tissue. Its cells are long and spindle-shape with a single nucleus. Its contraction is involuntary. It can be found in blood vessels walls, in the digestive tube, etc.
Skeletal muscle tissue. It is compounded by long striated cells with multiple nuclei. Its contraction is voluntary. It is located in skeletal muscles which make able the movement.
Cardiac muscle tissue. Cells are striated with a single nucleus and they are jointed together making a net. Its contraction is involuntary. It forms the heart.
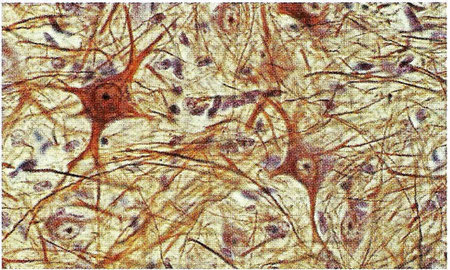
d) Nervous tissue
It detects the changes in the internal and external environment and transmits orders through the body. It is formed by two types of cells:
- Neurons, which function is to transmit the nervous impulse
- Glial cells, which provide support to neurons (defence, nutrition, etc)
http://youtu.be/otoiSr7lb88
(video sobre tejidos)

READING ACTIVITIES
After read the text, copy and answer the following questions on your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
4.1. Why blood is considered a connective tissue?
4.2. Make a comparative table of kinds of muscle tissues.
You have to compare cells, location, function and type of contraction.
4.3. Listen and decide what type of tissue is been described:
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




