1. The reproduction function
The reproduction function is the set of processes that allow living beings to produce offspring. It is essential to ensure the survival of the species, so that new individual will replace those who die.
Human reproduction is sexual. That means that to perpetuate our species, it is necessary for two individuals of different sex, male and female, to take part. Each of them produces a type of reproductive cell or gamete.
Reproduction involves five processes:

• Gametogenesis. This is te process of forming gametes (ovum and spermatozoon). This formation takes place in the gonads, specialised male (testicles) and female organs (ovaries).
• Fertilisation. This is the joining of two gametes (an ovum and a spermatozoon) and the formation of the first cell of the new individual (zygote). Fertilisation is internal: it takes place inside the female reproductive system.
• Embryo development. Cell division increases the number of cells that make up the zygote, which becomes an embryo. We are viviparous. This means that the embryo continues developing inside the woman's uterus and becomes a foetus (gestation).
• Childbirth. This is the birth of the baby. Human beings are live-bearing. The baby is born alive and fully formed.
• Development. The baby grows and reaches maturity. This process covers several stages from birth to adulthood.
a) The beginning of reproductive life
When a baby is born, its reproductive organs are already formed. These reproductive organs are called the primary sexual characteristics.
However for people to reproduce, these organs must mature and produce sex cells. This stage is known as puberty.
- In girls, it starts at around 10 to 13 years of age.
- In boys, it stars at around 12 to 14 years of age.
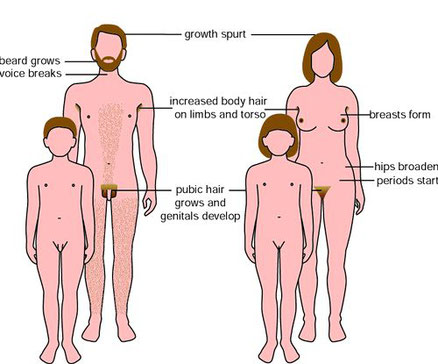
During puberty, the body matures sexually. The reproductive organs begin to produce sexual hormones. These hormones cause secondary sexual characteristics to develop:
• In girls, breasts and external genitalia develop. Hips widen and pubic and underarm hair grows.
• In boys, bones thicken and muscles grow. Voice deepens, pubic and underarm hair grows. Hair grows on face and chest.
Adolescence extends from puberty to adulthood. During this stage, physical maturity is accompanied by psychological and social changes. Sexual desire appears. We feel the need to explore our body and we need the support of our friends. We also begin to question decisions made by the adults around us.
b) The end of reproductive life
Men produce spermatozoa throughout almost their whole life, although the quantity and quality of these gametes decrease gradually after 50 years of age.
Women, on the other hand, stop ovulating and therefore menstruating at between 45 and 50 years of age. This period is known as menopause.

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
1.1. Explain the meaning of these sentences:
a. Human reproduction is sexual
b. Human fertilisation is internal
c. Human embryonic development is viviparous
1.2. Listen and complete the text:
|
Psychological changes
During ……………………………, teens experience increases in both physical and psychological …………………………… This involves ……………………………… changes, as ………………………… levels increase, ………………………… changes occur affecting ………………………… and personality.
These ………………………… are responsible for the adolescent drive for ……………………………, which often leads to ………………… with adults as adolescents reaffirm their …………………….
|
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




