3.3. Fertilisation
Fertilisation is the fusion of the spermatozoon and the ovum to form the zygote. This process takes place in the Fallopian tubes.
In order for the spermatozoa reach here, it is necessary the release of semen (ejaculation) inside the vagina. This occurs during the sexual intercourse (coitus or copulation).
From the vagina, spermatozoa go up through the uterus until they reach the Fallopian tubes. If the meet an ovum here, fertilisation may take place.
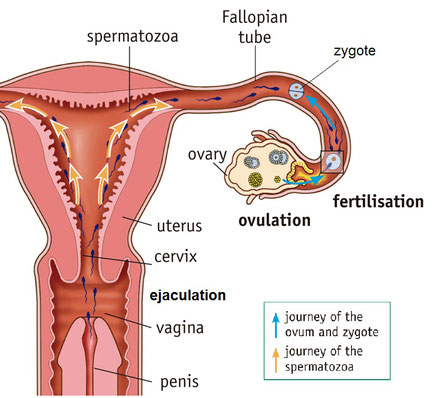
Spermatozoa only live for 4 days after ejaculation and the ovum only lives for 2 days after ovulation. This means that the gametes must come together during this time, to fertilisation occurs.
The first of the spermatozoa that touch the ovum releases the enzymes of its acrosome and breaks the protective covering of the ovum allowing the spermatozoon’s nucleus to enter. Immediately the nuclei of both gametes fuse and zygote is formed. Once fertilised a chemical barrier is formed around the ovum to prevent other spermatozoa entering.

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.5. Answer the following questions:
a. Where does fertilisation usually take place?
b. How is semen released?
c. How long do spermatozoa live for?
d. How long does an ovum live for after ovulation?
e. What is a fertilised ovum called?
3.6. Listen and find the ten mistakes in the text:
|
Fertilisation
Fertilisation is the name given to the join of an ovum and a spermatozoa, which creates a zygote, the first stage of an embryo. Of the hundreds of millions of sperm deposited in the uterus, a few hundred will manage to get through the uterus and reach the Fallopian tubes to meet the ovary.
Only one of these gametes will manage to pass through the thick layer that protects the ovum. When a sperm has entered, the properties of the outer membrane of the ovum change to prevent other sperm from entering.
Sperm can stay alive for about five days after ejaculation, so fertilisation is also possible if copulation takes place a few days before menstruation.
|
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




