2.1. Cells of the nervous
system
The nervous system is formed by two types of cells:
- neurons (the proper nerve cells)
- glial cells
a) Neurons:
Neuron is the anatomical and physiological unit of the nervous system. They form the 90 % of it.
- Parts of a neuron
- Dendrites. They are numerous thin and branched prolongations. They receive the nerve impulse from other neurons.
- Soma. It the cell body. It integrates the information.
- Axon. It is a long and single prolongation. It transmits the nervous impulse. Its end is branched.
- Synaptic terminal. It is a protuberance located at the end of axonal branches. From here, the nerve impulse is transmitted to other neuron.

- Types of neurons
According to its structure, a neuron can be:
- Multipolar neuron. They are most abundant. They have numerous dendrites, and one axon. They are usually motor neurons.
- Bipolar neuron. They have a dendrite and an axon. They are usually interneurons.
- Unipolar neuron. They do not have dendrites. They are usually sensory neurons.
Other criterion to classify neurons is their function:
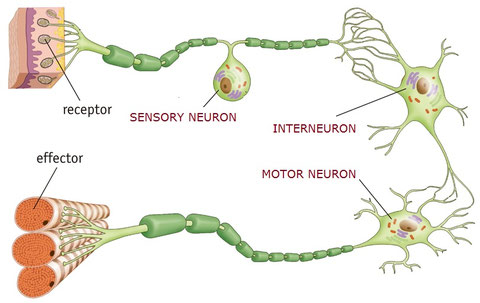
- Sensory neuron. They carry the nerve impulse from receptors to nerve centres. They form nerves.
- Motor neuron. They carry the nerve impulse from nerve centres to effectors. They form nerves.
- Interneuron. They are located connecting neurons. They form the nerve centres.
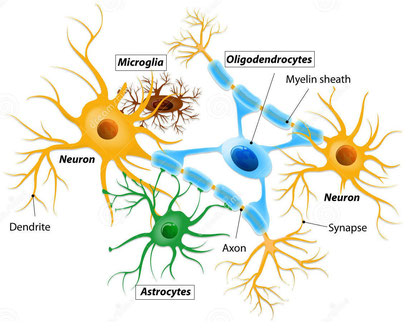
b) Glial cells (Neuroglia)
They represent the 10% of the nerve tissue cells.
These cells are in direct contact with neurons and surround them.
They support, nourish and protect neurons (astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, etc).
Some of them form myelin sheath (Schwann cells) and others make cerebrospinal fluid.

ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
2.3. Look at the picture and identify what each number represents.
Now listen and indicate which part of the neuron is described.
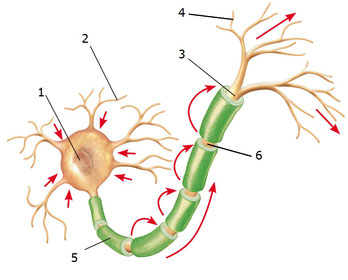
2.4. What represent the arrows in the picture of the previous activity?
2.5. Myelin sheath forms an insulating layer that covers the axon.
Then, how is nerve impulse transmission possible?
Does this substance give any advantage?
2.6. Interneurons are also called “association neurons”.
Explain the reason for this name.
2.7. Listen and identify the type of neuron that is described.
a. Interneuron
b. Motor neuron
c. Sensory neuron
2.8. What is the function of glial cells? Could neurons survive without them?
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




