2.1. Biomes of frigid
zones
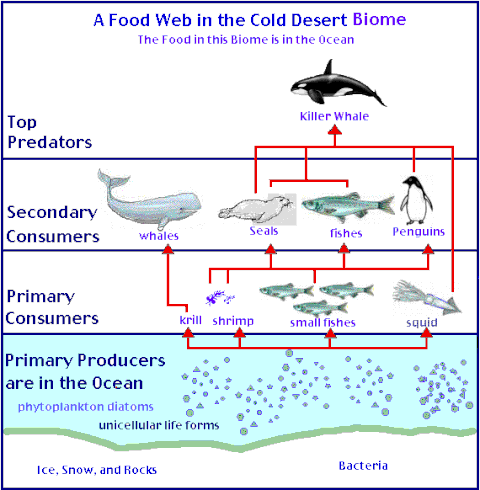
a) Cold desert
It extends for the Polar Regions (Arctic and Antarctic).
The climate is characterised by long and extremely cold winters with very scarce precipitations.
The soil is frozen and covered by ice. And in the most part of the Arctic regions there is not continent, only the ice cap.
There is no vegetation and the food web is aquatic.
The fauna is formed by whales, seals, fish, penguins and polar bears.
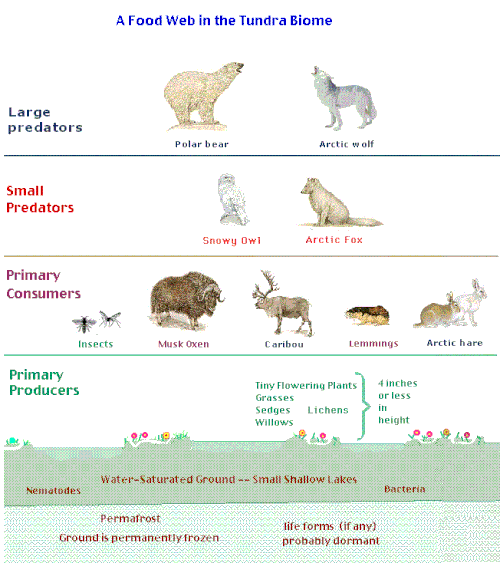
b) Tundra
Arctic tundra is found in sub polar regions. Alpine tundra is found in the high mountain areas of temperate regions and even in the tropics.
The tundra has long, very cold winters and very short summers.
The ground in the arctic tundra is permanently frozen (permafrost), so deep-rooting plants, for example trees, cannot survive.
The main plants which grow here are mosses and lichens. There are also some shrubs in the more temperate regions of alpine tundra.
The reindeer or caribou, the wolf, the polar fox and the arctic hare are some of the typical animals of the arctic tundra.

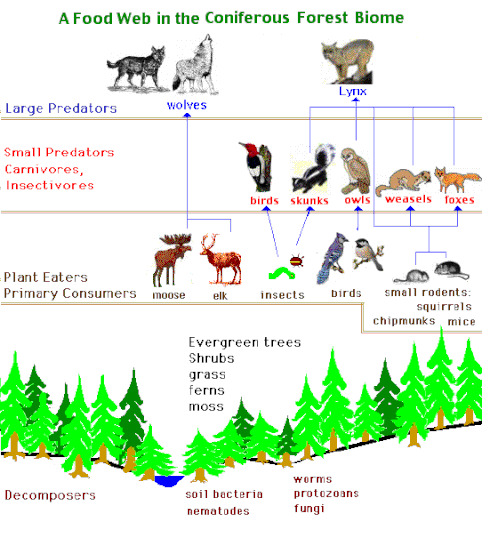
c) Taiga (Boreal forest)
This type of forest is found in very cold regions and in high mountain areas which have long winters with heavy snowfall and short, wet, and temperate summers.
Taiga forests extend north of a latitude of 45° (subarctic zone) and cover almost the entire northern hemisphere.
The main types of trees found in these forests are conifers (fir trees and pines). There are not very many shrubs, but there are many lichens and mosses.
It is difficult for decomposers to function in these forests, because the leaves of the trees are extremely hard and the temperatures in these regions are very low. This means that the transformation of organic matter into inorganic matter is a very slow process. For this reason, the soil is rich in humus but poor in mineral matter.
The typical fauna of this region consist of elk, deer, hares, foxes, wolves, bears, marmots, etc.


READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
2.2. Why are considered the Poles as deserts if they have a lot of water?
2.3. Why is impossible to find trees in the tundra?
2.4. In extremely cold winters, with the water in the form of ice, only conifers can
survive.They are pyramid-shaped and evergreen trees with needle-like
leaves. Both, shape andleaves are adaptations to the intense snowfall
and to the lack of water respectively. Explain why.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




