3.2. Earthquakes
Earthquakes are sudden movements of the surface layers of the Earth. They occur when large rocky masses inside the Earth’s crust move past each other.
The movement of these rocky masses releases a large amount of energy, and this can be sudden, violent and destructive.
a) Elements of an earthquake
An earthquake has the following elements:
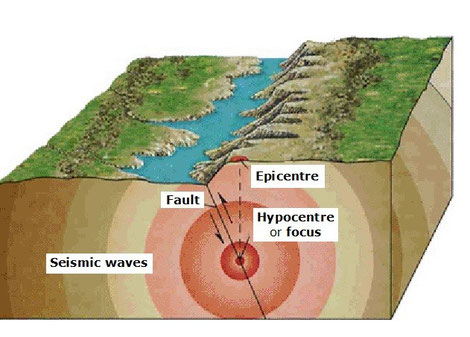
- The hypocentre (or focus) is the point in the Earth’s crust where
the earthquake starts and it produces seismic waves.
At an earthquakes hypocentre the rocks break up, which causes
the ground to move violently, and energy is released.
- The epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface that is directly
above the hypocentre. The epicentre is the place where the seismic waves
first reach the Earth’s surface and the effects of the earthquake are felt
most intensely.
- The seismic waves are vibrations that extend in all directions
from the hypocentre. When they reach the surface, they produce catastrophes.
b) Measuring of an earthquake
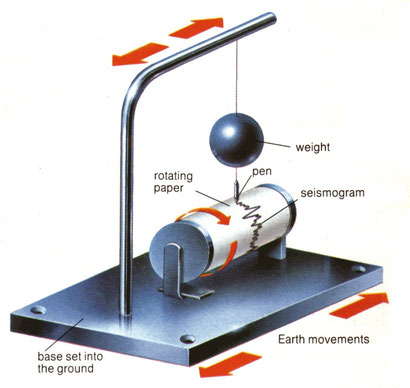
Seismographs are the devices that geologists used to detect and record
earthquakes. A seismograph consists of a hanged weight with a pen which draws
on a roll of paper located below.
During the shake, the base of the seismograph and the roll of paper move
but not the weight, so that the pen draws squiggly lines on the paper,
creating a record of the earthquake. This graph is called a seismogram.
We can use two different parameters to measure earthquakes:
- The magnitude of an earthquake tells us how much energy is released
during a tremor. We use a 9-degrees scale (Richter scale) to measure
the magnitude of an earthquake. On this scale, each number represents
a release of energy that is 10 times more than the previous number.
- The intensity of an earthquake is determined by studying how much
destruction it causes. To express intensity we compare the various levels
of destruction caused by an earthquake with a 12-degree scale
of descriptions (Mercalli scale). This scale is not very reliable because
the destruction caused depends on factors like the quality of the constructions.
Animation: Mecalli scale (elearning)
c) Danger of earthquakes
An earthquake is one of the natural disasters that can cause most death
and destruction, mainly because they can provoke buildings collapse,
landslides, floods, fires, etc. If the earthquake occurs under the sea floor,
tsunamis can destroy coastal areas.
As it is extremely difficult to predict earthquakes, there are some measures
to prevent earthquakes disasters. The main ones are:
- Elaborate earthquake risk maps that indicate areas of high risk.
- Build earthquake-resistant buildings.
- Develop civil protection programmes for catastrophic situations.
- Inform people about the measure they should adopt during and after
an earthquake.

READING ACTIVITIES
After reading the text, copy and answer the following questions into your notebook:
Remember: you must make complete sentences.
3.3. Indicate the differences between:
a. Hypocentre - Epicentre
b. Magnitude of an earthquake - Intensity of an earthquake.
3.4. Listen and identify which of the two terms of each couple is been described:
a. Tide / Tsunami
b. Richter scale / Mercalli scale
c. Seismic waves / Coastal waves
d. Hypocenter / Epicenter

Now,
check
your
answers!

INTERACTIVE ACTIVITIES
Clic the link and answer quiz's questions:
Fukusihima (Linguaframe)

LISTENING ACTIVITIES
Download this worksheet
and complete it,
while you listen this audio.
 BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)
BIOGEOSPHERE
Bilingual Biology and Geology
I.E.S. "J.S.Elcano (Sanlúcar Bda.)




